Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


In patients with chronic hepatitis B, a four-week monotherapy of JNJ-64530440 was well-tolerated and attained significant antiviral activity.
According to the findings of a recent study, oral administration of JNJ-64530440 (a novel hepatitis B virus capsid assembly modulator) for 28 days demonstrated considerable hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA and RNA reductions and was well-tolerated in treatment-naive people with chronic hepatitis B (CHB). The researchers aimed to investigate the pharmacokinetics, safety and antiviral effect of JNJ-64530440 in CHB.
In this phase 1b trial, 20 treatment-naive, HBeAg-positive or -negative people suffering from CHB were randomly segregated into two groups: (i) JNJ-64530440 group (once-daily/twice-daily): Given 750 mg JNJ-64530440 once or twice everyday, and (ii) Placebo group. All the patients (mean age= 43.8 years) completed dosing/28 days of follow-up.
Mild-to-moderate treatment-associated side effects such as elevated alanine aminotransferase, fatigue, headache, and decreased neutrophil count were observed in 6/8 once-daily group, 4/8 twice-daily group, and 3/4 placebo group. A considerable reduction in HBV DNA was seen, as shown in Table 1.
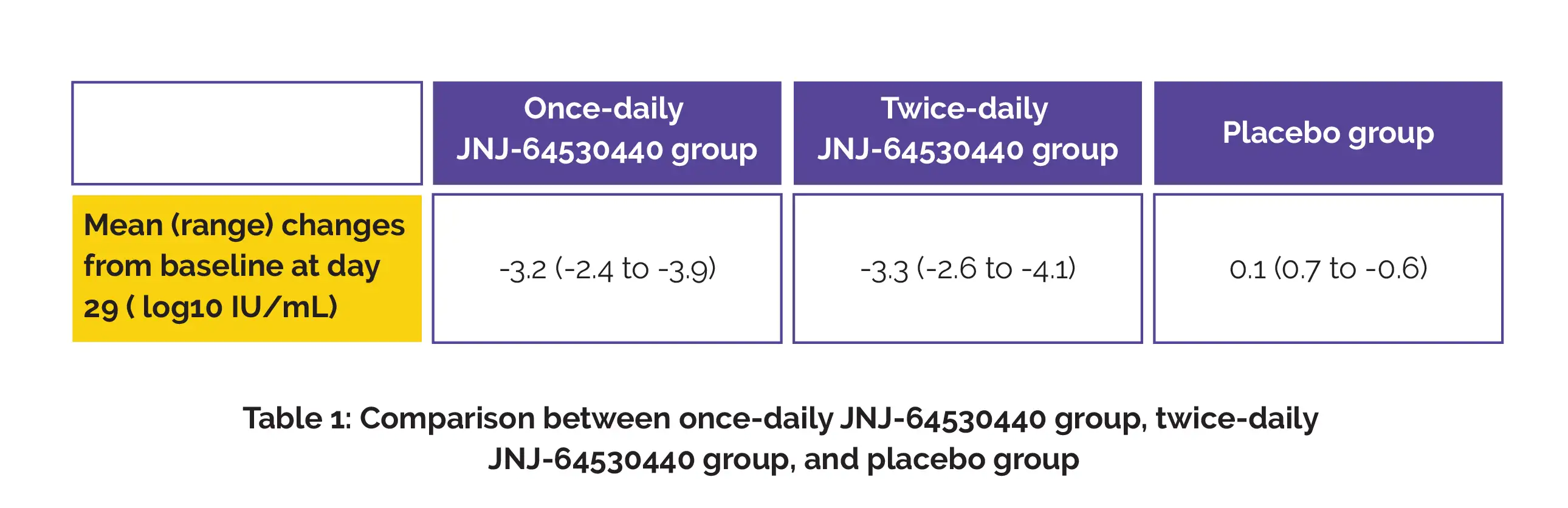
The levels of HBV DNA observed were under the lower limit of quantification in 5/8 once-daily group and 3/8 twice-daily group. On day 29, the mean (standard error) changes versus baseline in HBV RNA for people with detectable baseline HBV RNA were -2.65 (0.81) log10 copies/mL in the once-daily group and -2.94 (0.33) log10 copies/mL in the twice daily group.
The levels of HBV RNA were noted to be 'target not detected' in 3/7 (twice-daily) group and 4/6 (once-daily) group. JNJ-64530440 pharmacokinetics were similar in CHB patients and healthy volunteers. JNJ-64530440 affects the formation of capsid, reduces the liberation of HBV-RNA-containing particles, and thus appears to be beneficial for the management of people infected with CHB.
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy
Safety, antiviral activity and pharmacokinetics of JNJ-64530440, a novel capsid assembly modulator, as 4 week monotherapy in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection
Ed J. Gane et al.
Comments (0)