Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


A randomized and double-blind clinical study was conducted to compare the analgesic effectiveness of Desmopressin and Ketamine to relieve renal colic.
Ketamine exhibits positive pain-relief outcomes in patients with renal colic. It provides superior pain management when compared to Desmopressin, although Desmopressin displays promising effectiveness during the initial minutes of treatment.
A randomized and double-blind clinical study was conducted to compare the analgesic effectiveness of Desmopressin and Ketamine to relieve renal colic.
Overall, 135 patients diagnosed with renal colic with the mean (standard deviation) age of 44.1±11.4 years, and of whom 82 (60.7%) were men were enrolled in the study. These volunteers received medical care at the emergency department. They were subsequently allocated at random to one of the three groups.
Subjects in the Desmopressin group received Desmopressin intranasally alongside Ketorolac intravenously, while patients in the Ketamine group received Ketamine intranasally in conjunction with Ketorolac. People in the control group, on the other hand, were administered Ketorolac along with an intranasal placebo. Vital signs were monitored both at the outset and after 60 minutes, and pain levels were evaluated at the start, as well as at 10, 30, and 60 minutes following treatment.
The mean scores on the visual analog scale (VAS) were notably reduced at 10, 30, and 60 minutes for the Ketamine group compared to both the control group and the Desmopressin group, as depicted in Table 1:
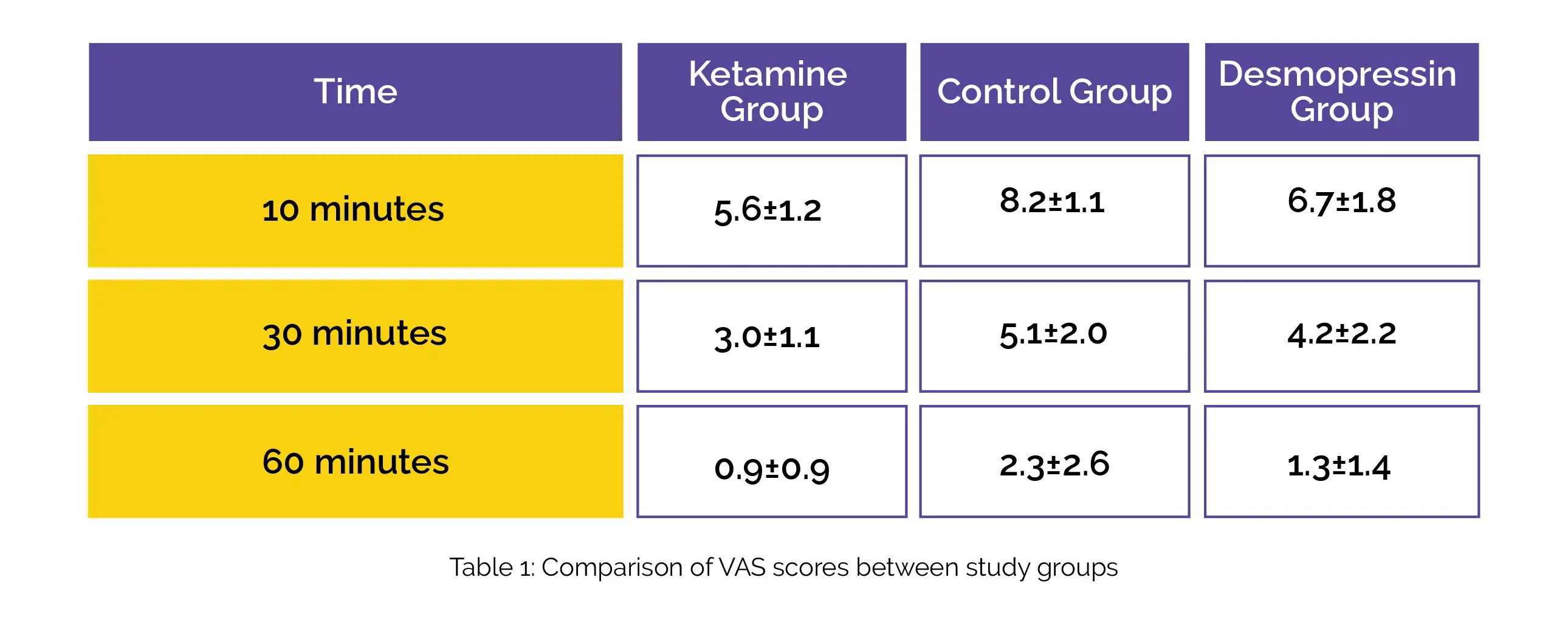
However, it's worth noting that the difference in mean pain scores between the Desmopressin group and the control group was only meaningful at the 10-minute mark post-treatment. There were no clinically significant variations in vital signs observed 60 minutes following treatment.
Ketamine exhibited superior analgesic effects in renal colic patients compared to Desmopressin, even though Desmopressin demonstrated efficacy during the initial minutes after treatment.
Clinical and Experimental Emergency Medicine
A comparative study of intranasal Desmopressin and intranasal Ketamine for pain management in renal colic patients: A randomized double-blind clinical trial
Farhad Heydari et al.
Comments (0)