Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


The effectiveness and safety of Tegoprazan-based bismuth quadruple therapy (TBMT) and Lansoprazole-based bismuth quadruple therapy (LBMT) were compared in eradicating Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori).
Tegoprazan-based bismuth quadruple therapy shows a non-inferior eradication rate and comparable adverse events to Lansoprazole-based bismuth quadruple therapy when used as the primary regimen for H. pylori management.
The effectiveness and safety of Tegoprazan-based bismuth quadruple therapy (TBMT) and Lansoprazole-based bismuth quadruple therapy (LBMT) were compared in eradicating Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori).
The study included adults aged 18 and above who had an H. pylori infection and no prior history of H. pylori elimination. Either Giemsa staining or rapid urease test was utilized to diagnose H. pylori illness. A total of 217 participants were randomized to receive either TBMT (n = 108) or LBMT (n = 109).
In this randomized, double-blind, active-controlled study, TBMT demonstrated greater rates of elimination than LBMT. Table 1 illustrates the elimination rates of TBMT and LBMT in the per-protocol (PP), corresponding modified ITT, and intention-to-treat (ITT) analyses.
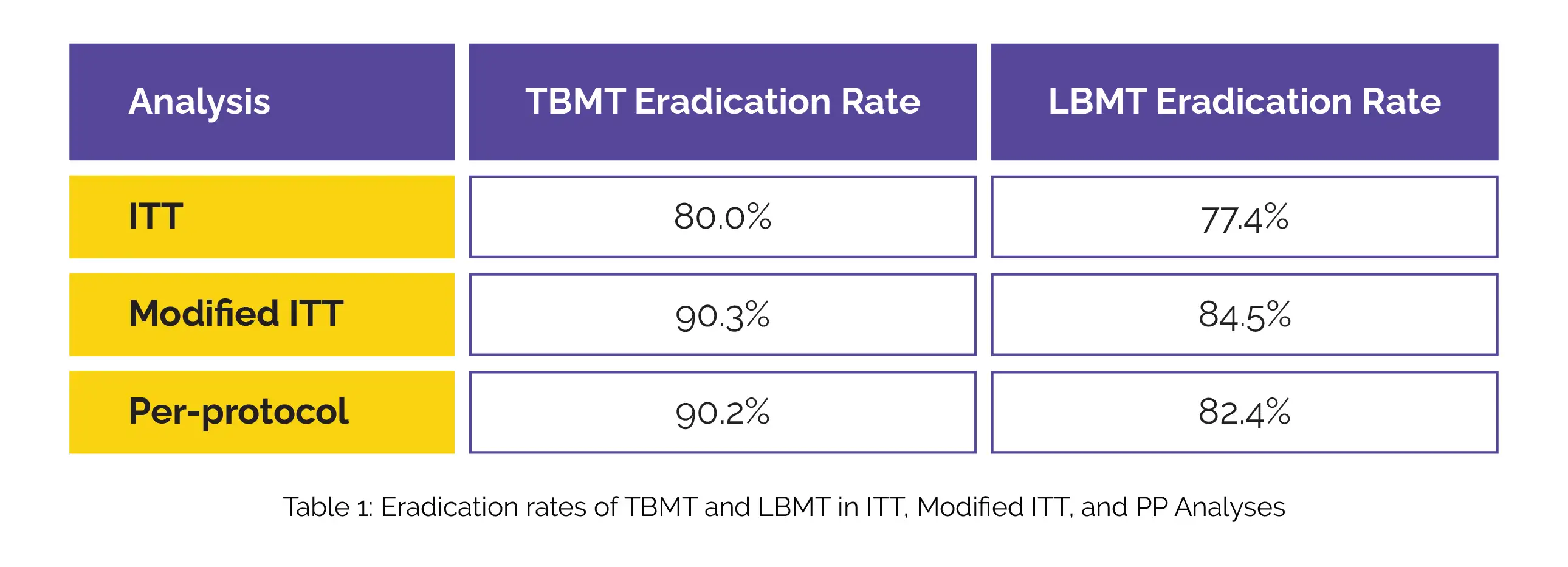
The occurrence of adverse events did not significantly differ between TBMT and LBMT groups (39.1% vs. 43.4%).
TBMT exhibited a non-inferior elimination rate and comparable occurrence of adverse events to LBMT as a first-line elimination regimen. The findings suggest that the substitution of proton pump inhibitors with Tegoprazan in bismuth quadruple therapy could lead to better elimination rates.
Helicobacter
Efficacy of tegoprazan-based bismuth quadruple therapy compared with bismuth quadruple therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection: A randomized, double-blind, active-controlled study
Joon Sung Kim et al.
Comments (0)