Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


The digital age has witnessed an unprecedented rise in technological innovations, shaping the essence and nature of human-computer interaction. [1] Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a formidable force in the modern world, making significant strides and becoming an integral part of various domains. [2] With AI integration, healthcare practices are experiencing unprecedented advancements, ultimately leading to better patient care and outcomes. [3] As society moves towards a future driven by AI, the emergence of advanced conversational AI models has become a prominent topic of academic discourse.
This transformative technology has remarkably transformed our interactions with machines and has profound implications across various fields. [1] An example of AI-driven progress in healthcare is chatbot emergence. It is an AI-powered tool that utilizes automated rules, natural language processing (NLP), and machine learning to process data and provide responses to various types of requests. In recent years, chatbots have been employed by numerous companies, including those in the healthcare industry, for tasks such as customer service, request routing, and information gathering. [3] These virtual assistants aid healthcare professionals in managing their responsibilities and improving patient satisfaction. [4]
On 30 November 2022, San Francisco-based company OpenAI created an AI chatbot tool called Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer (ChatGPT). [5-7] The introduction of this newest language model has sparked contemplation among individuals regarding the fascinating (yet potentially challenging) transformations that AI could bring to our lives in the future. [5] This AI-powered chatbot possesses vast capabilities and is creating a buzz across all occupational sectors. [8,9] With an impressive parameter count of 175 billion, this model stands as one of the largest and most potent options for AI processing in various professional fields, contributing to its increasing adoption across different occupations. [9]
It is a language model that utilizes deep learning for generating responses to text-based prompts, closely resembling human-like language. Given ChatGPT's proficiency and versatility in generating natural language, it has emerged as an ideal tool for personalized healthcare applications. [10] Leveraging the capabilities of machine learning, ChatGPT has surpassed the constraints of conventional chatbots, enabling more human-like and engaging conversations. [1]
ChatGPT has garnered considerable attention for its versatile performance in various natural language tasks. [11] Its triumph signifies the advancement of AI chatbots that operate on natural human language. Its remarkable achievement of attracting one million users in a mere five days following its launch is a testament to its practicality in everyday activities. This overwhelming response was further exemplified by a rapid surge to 100 million users within a span of two months, thus establishing itself as the most rapidly growing consumer application in history. [5,12]
To gain a comprehensive understanding of the capabilities of ChatGPT in the healthcare sector, it is crucial to delve into its origins and the underlying technology that powers it. [4]

The name "ChatGPT" reflects its nature as a chatbot, which is a program capable of comprehending and generating text-based responses. [13] It is a sophisticated machine learning model renowned for its exceptional accuracy in natural language generation (NLG) tasks. By utilizing the inputs it receives, ChatGPT produces text that mimics human language. [7] Anecdotal evidence suggests that ChatGPT exhibits qualities of deductive reasoning, coherent chain of thought, and the ability to recognize long-term dependencies. [11]
It outshines its earlier Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT)-based counterparts due to its proficiency in handling multiple languages, resulting in refined and highly sophisticated responses through advanced modelling techniques. [13] This revolutionary AI chatbot is indeed a game-changer and transformative innovation. Thanks to its incredible creativity and fluency! [14]
ChatGPT relies on the GPT architecture, a neural network framework specifically engineered to process natural language and produce output that is contextually relevant. [13] It leverages a vast array of data from diverse sources, processing it through a transformer model to establish connections between different pieces of information and make informed predictions about appropriate text generation in various contexts. [15]
The initial training of ChatGPT involved an extensive dataset sourced from the internet, utilizing supervised learning techniques. Following this, the model underwent training via reinforcement learning with human feedback, leading to the creation of a reward model specifically for reinforcement learning. [7] Unlike previous AI models primarily based on Deep Learning, ChatGPT belongs to a new category known as Large Language Models (LLMs). LLMs are designed to predict the probability of a given word sequence by leveraging contextual information from preceding words.
When trained on extensive text data, LLMs can generate novel word sequences that have not been explicitly seen by the model but align with the natural patterns of human language.
ChatGPT specifically relies on GPT3.5, an LLM trained on the extensive OpenAI 175B parameter foundation model, which encompasses a vast corpus of internet text data. The training process employs reinforcement and supervised learning techniques. [11]
The purpose of ChatGPT, a recently launched chatbot, is to make our life simpler. [15] ChatGPT exemplifies generative AI as it has the skill to generate entirely novel content by organizing existing information in innovative ways. [3] This AI language model leverages extensive internet-based metadata and its distinguishing feature lies in its capacity to comprehend inputs in natural human language and generate outputs that are easily understood by humans. [12] It is specifically designed to produce text that closely resembles natural human language, enabling its application in various language-related tasks such as translation, summarization, and dialogue systems.
It has the capability to generate responses in chatbots, provide answers to questions, and even author creative narratives. Through extensive training on a vast corpus of online text data, ChatGPT achieves a remarkable level of text quality that is comparable to that produced by humans. The underlying technology, known as GPT, excels in processing sequential data, particularly in the form of natural language, allowing ChatGPT to grasp the contextual nuances within sentences and generate coherent text accordingly. [2]
Embracing AI-powered tools like ChatGPT is pivotal to create better patient-centered healthcare systems. [4] The inevitable prevalence of LLM technology, encompassing the extensive adoption of ChatGPT, is poised to revolutionize healthcare practice, education, and research. [13] Being an AI tool, it engages in natural human language interactions. Its recent introduction has sparked significant enthusiasm and widespread adoption. [12]
ChatGPT's ability to generate human-like responses across a wide range of inquiries makes it a valuable tool for healthcare applications. Its transformative impact on the delivery of care is evident in various aspects of the healthcare sector. [16] Let's explore some of the uses of ChatGPT in healthcare and delve into the benefits it brings to patients, doctors, and researchers.
1. Medical record-keeping: ChatGPT has the potential to optimize the medical record-keeping process by generating medical histories, clinical notes, and automated summaries of patient interactions. Healthcare professionals, including nurses and doctors, can dictate their notes, and ChatGPT can extract and summarize crucial details automatically, such as symptoms, diagnoses, and treatments.
Furthermore, it can aid in extracting pertinent information from patient records, such as laboratory results or imaging reports, thereby improving the efficiency and precision of medical data management. [16] Such streamlined documentation aids in optimizing time and minimizing the risk of human error associated with manual documentation processes. [2]
2. Disease surveillance: ChatGPT can contribute to disease surveillance efforts by enabling medical experts and the general public to monitor global health data in real time. Through the analysis of extensive data from various sources, including news reports and public health databases, ChatGPT possesses the capability to detect patterns and anomalies that could indicate the emergence or propagation of diseases. This enables ChatGPT to deliver automated alerts to public health officials, medical care providers, and the general public, empowering them to take prompt measures in order to mitigate the spread of diseases.
3. Virtual assistants for telemedicine: ChatGPT can be harnessed to create virtual assistants that help patients in scheduling appointments, managing treatment plans, and organizing their health information. As telemedicine gains popularity, patients can rely on these virtual assistants powered by ChatGPT to receive personalized guidance and support, thus enhancing their remote healthcare experience.
4. Medication management: Patients often face difficulties in handling multiple medications and adhering to dose instructions. ChatGPT can play a crucial role in assisting patients with medication management. It can provide valuable support by offering medication reminders, precise dose instructions, and information regarding possible adverse effects. Furthermore, it can offer insights into drug interactions, contraindications, and other essential considerations to support patients in effectively managing their medications.
5. Patient triage: ChatGPT can assist in patient triage by asking relevant questions about symptoms and medical history, enabling healthcare professionals to determine the urgency and severity of a patient's condition.
6. Clinical trial enrollment: Enrollment for clinical trials can be a perplexing task. ChatGPT can simplify this process by analyzing patient data and discovering potential participants who fulfill the eligibility criteria for specific trials. Leveraging ChatGPT's capabilities in clinical trial recruitment can boost efficiency, particularly in reaching diverse populations.
7. Medical writing and documentation: ChatGPT is useful to assist medical care personnel in writing and documenting medical reports, like discharge summaries and clinical notes. By offering real-time suggestions and corrections, it streamlines the process of medical writing, ensuring accurate and efficient documentation. [16]
By streamlining the research process, ChatGPT offers a time-saving solution that aids researchers in organizing the structure of their articles. It provides valuable guidance on various sections, including title, abstract, introduction, method, results, and discussions, facilitating the completion of scientific writing with enhanced speed and accuracy. Moreover, for researchers whose native language is not English, ChatGPT can serve as a beneficial auxiliary tool, supporting the improvement of their writing skills. [17]
8. Creating symptom checkers: ChatGPT can be harnessed to create virtual symptom checkers, assisting people in comprehending their symptoms and ascertaining whether it is necessary for them to seek medical attention. These symptom checkers can offer guidance on the next steps, encompassing self-care measures, before seeking professional medical assistance.
9. Drug information: ChatGPT has the capability to offer up-to-date information on medications, encompassing details regarding side effects, interactions, and contraindications. Individuals can engage in natural language conversations with ChatGPT, receiving precise and timely information to make well-informed decisions regarding their medicines. Moreover, healthcare providers can leverage ChatGPT to stay abreast of novel medications, drug recalls, and significant advancements in the pharmaceutical industry.
10. Clinical Decision Support: As a useful tool for medical care providers, ChatGPT has the capacity to deliver real-time recommendations based on evidence-based practices. [16] While the ultimate responsibility for medical decisions rests with clinicians, ChatGPT can provide valuable support by offering suggestions and recommendations for treatment based on patient symptoms and medical history. [2]
It can suggest suitable treatment options for specific conditions, alert healthcare professionals about potential drug-drug interactions, and offer clinical guidelines for complex medical cases. This support empowers clinicians in informed decision-making, hence leading to improved patient outcomes. [16]
11. Mental health support: ChatGPT offers various possibilities for its application in mental health, including the potential to diagnose mental illness and provide support during therapy sessions. [15] It has the capability to provide behavioral health assistance through tasks such as mental health condition screening, offering coping strategies, and facilitating connections with supplementary support resources for patients. [16] By offering personalized responses tailored to individuals seeking therapy, ChatGPT eliminates the need for expert therapists in some cases.
Additionally, healthcare professionals and counsellors can potentially achieve more accurate diagnoses by analyzing a person's conversational patterns and developing specialized treatment plans over time.
Harnessing the full potential of ChatGPT enables us to redefine how we connect with our inner thoughts and discover empathetic paths towards recovery. It presents the potential of being a potent tool for bolstering overall well-being and mental health. When used appropriately, ChatGPT can enhance communication, facilitate individuals' understanding of their thoughts and emotions, and teach effective coping mechanisms for challenging situations. [15]
12. Patient Communication: ChatGPT can be employed to generate automated responses to patient inquiries, such as appointment scheduling and medication management. This helps enhance communication efficiency and improves the patient experience. It is crucial to emphasize that ChatGPT must be utilized as a supportive tool for medical care professionals and must not substitute their expertise and clinical judgment in making decisions. [2]
13. Remote patient monitoring (RPM): RPM is gaining popularity in improving the outcomes of patients and minimizing healthcare costs. ChatGPT can contribute to RPM by analyzing data from wearable devices, sensors, and other monitoring tools. It offers real-time insights into health status of the patient, allowing healthcare providers to intervene promptly if the condition of the patient worsens or concerning trends are detected.
14. Medical translation: ChatGPT has the potential to revolutionize medical translation by offering real-time language services that bridge the communication gap between patients and healthcare providers. With its advanced language processing skills, ChatGPT exhibits the ability to proficiently and promptly translate medical terms, technical terminology, and everyday expressions. This empowers patients to understand their diagnosis, explore treatment options, and comprehend medication instructions effectively.
15. Medical education: Lifelong learning is essential for healthcare personnel. ChatGPT can serve as an instant gateway to relevant medical information and resources, supporting students and medical care providers in their ongoing education and development. [16] Advancements in technology, particularly the emergence of AI models like ChatGPT, have opened up numerous valuable opportunities for the field of medical education. Here are a few ways in which ChatGPT can contribute:
(a) Automated Grading: ChatGPT can be harnessed to examine student papers and essays, analyzing aspects such as sentence structure, vocabulary, grammar, and clarity. This feature is particularly beneficial for educators who face the challenge of grading a large volume of assignments.
(b) Teaching Support: ChatGPT's capacity to generate exercises, quizzes, and scenarios can assist in classroom activities, yielding practice opportunities and assessments. Its ability to offer translations, explanations, and summaries also helps simplify complex learning material for students.
(c) Personalized Learning: By creating virtual tutors or assistants, ChatGPT can respond to students' queries and offer feedback on their work. It enables the development of personalized study plans and learning materials tailored to individual student's learning styles and abilities.
(d) Research Aid: ChatGPT serves as a valuable research assistant, answering questions, providing text summaries, generating bibliographies, and facilitating literature reviews and data analysis. Medical researchers can benefit from its ability to condense relevant articles and extract key findings, allowing efficient navigation through vast amounts of information.
(e) Quick Information Retrieval: ChatGPT provides rapid access to accurate and up-to-date medical information, covering a wide range of topics such as diseases, treatments, and procedures. This feature proves useful for medical students and professionals seeking immediate clarification or information on specific subjects.
(f) Case Scenario Generation: Utilizing ChatGPT, case studies and scenarios can be generated to enhance medical students' diagnostic and treatment planning skills. This helps them develop clinical reasoning abilities and better prepares them for real-world clinical situations.
(g) Content Creation for Learning: ChatGPT's ability to generate content aids in the creation of summaries, quizzes, and flashcards, empowering educators to develop relevant, engaging, and interactive materials to facilitate student learning.
(h) Language Translation: ChatGPT's effective language translation capabilities can assist medical professionals and educators in communicating with patients from diverse linguistic backgrounds, ensuring optimal medical care provision. [2]
16: Revolutionize the digital health sector: The implementation of ChatGPT holds the potential to transform the digital healthcare industry and alleviate the burden on physicians, addressing issues like burnout. By automating time-consuming tasks and enabling more efficient communication with patients, ChatGPT can enhance the overall experience for doctors and patients alike. While the utilization of ChatGPT in healthcare represents just the beginning of an era of AI-driven medicine, it is crucial to maintain human oversight of the outcomes it generates.
AI has exhibited applications in a multitude of domains, suggesting endless possibilities and a promising future. With ongoing advancements in machine learning techniques and training on new datasets, ChatGPT will continue to enhance its ability to comprehend human language and provide appropriate and meaningful responses. The model is poised to become even more intelligent, capable of addressing a wider range of inquiries and fulfilling diverse requests. The potential future developments of ChatGPT are extensive, and observing the app's continual evolution and refinement is truly fascinating. In fact, ChatGPT formulates its responses in a manner that closely resembles human-like sentences, promoting greater recognition and understanding by users. [15]

AI systems have the potential to remarkably enhance medical care and boost health outcomes. Hence, it is of utmost importance to ascertain that the advancement of clinical AI adheres to principles of explainability and trustworthiness. Examining the medical knowledge of AI systems in comparison to that of expert human clinicians serves as a vital initial measure in assessing these qualities. In this regard, an evaluation of ChatGPT was conducted employing the United States Medical Licensing Exam (USMLE) as a benchmark.
The USMLE is a rigorous and comprehensive three-step standardized testing program designed to assess clinicians' proficiency across diverse domains, including bioethics, medical management, foundational sciences, and clinical reasoning. The USMLE questions are meticulously designed to ensure consistency in difficulty and complexity, adhering to strict standards and regulations. This standardized nature of the exam makes it an excellent input framework for AI testing purposes. The three standardized tests are integral components of medical licensure in the United States, evaluating comprehensive medical knowledge at an expert level.
Notably, ChatGPT demonstrated performance levels near or at the passing threshold of 60% accuracy on the USMLE, marking a significant milestone in the advancement of AI. Importantly, ChatGPT achieved this outcome without relying on specialized input from human trainers. Additionally, it exhibited understandable reasoning and provided valid clinical insights, enhancing trust and explainability.
(1) ChatGPT yielded moderate accuracy approaching passing performance on USMLE
To assess the accuracy of ChatGPT on USMLE Steps 1, 2CK, and 3, the AI outputs were evaluated and classified as accurate, inaccurate, or indeterminate using the Accuracy, Concordance, and Insight (ACI) scoring system. Figure 1 yields an overview of ChatGPT accuracy performance on USMLE, presenting: (A) The distribution of accuracy for inputs encoded as open-ended questions, (B) The distribution of accuracy for the inputs encoded as multiple-choice single answer without justification (MC-NJ) or with forced justification (MC-J).
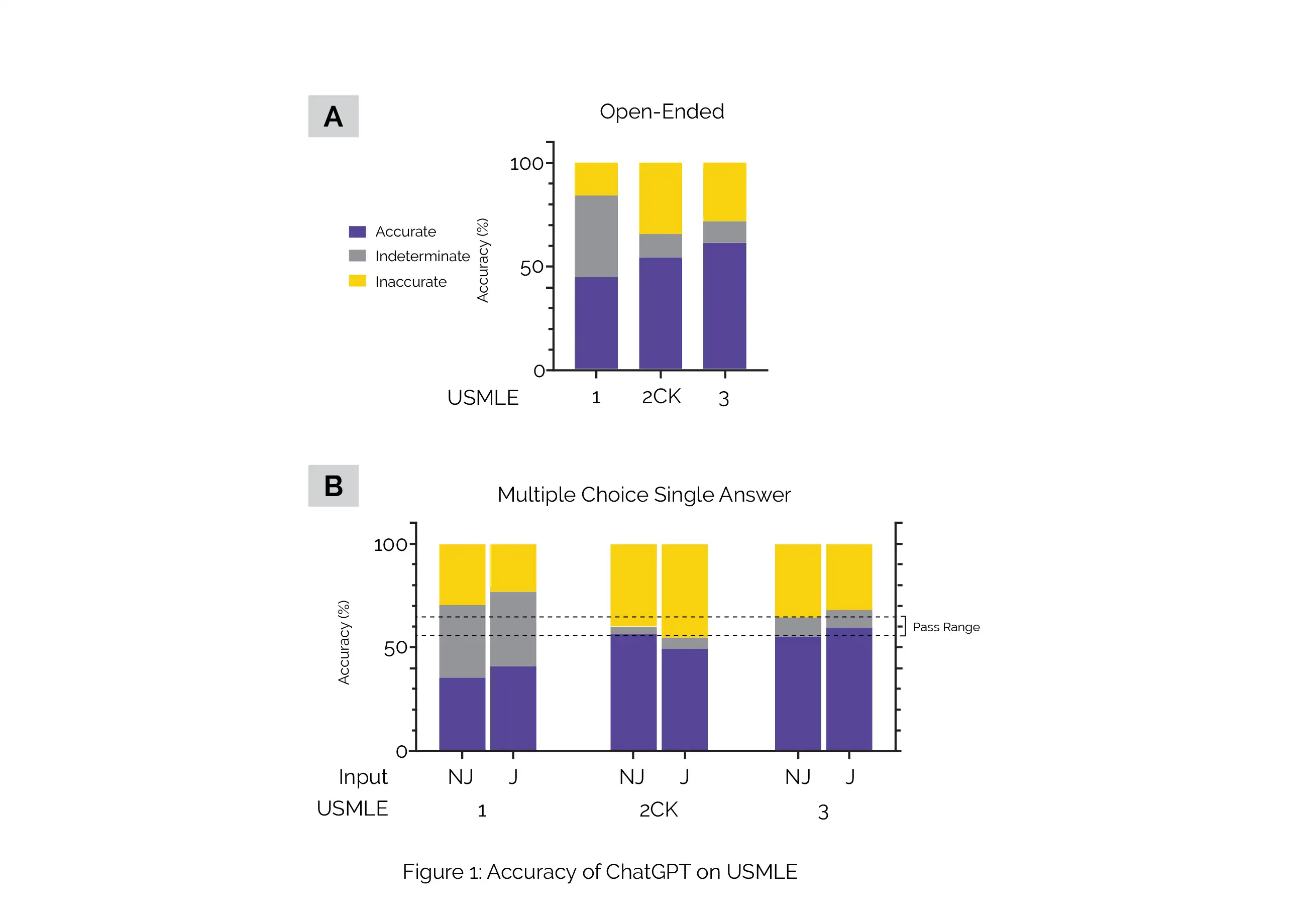
(2) ChatGPT demonstrated high internal concordance
ChatGPT demonstrated a notable level of agreement between its answers and explanations, indicating strong internal consistency within its probabilistic language model. Figure 2 visually represents this high internal concordance of ChatGPT, including: (A) General concordance across all exam types and question encoding formats, (B) Concordance rates distinguished between accurate and inaccurate outputs across all the exam types and question encoding formats. The statistical analysis using Fisher exact test indicated a significant difference (p < 0.001) between accurate and inaccurate outputs.
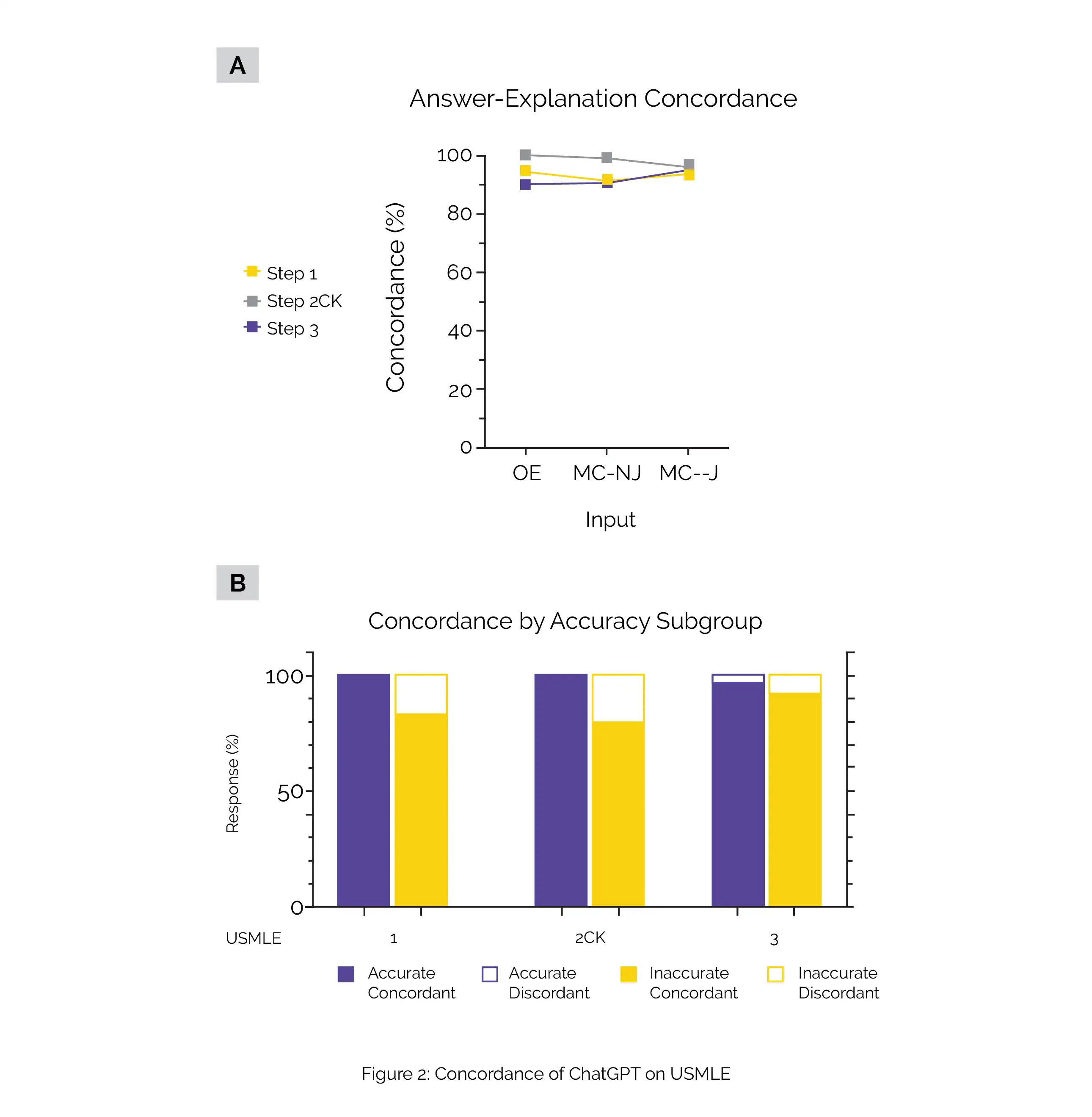
(3) Explanations generated by ChatGPT contained nonobvious insights
In general, ChatGPT generated at least one noteworthy insight in 88.9% of all responses. The frequency of insights remained relatively consistent across different exam types and question input formats. Across all exam types, it was observed that the average density of insights was considerably greater in accurately answered question items compared to inaccurately answered ones (0.458 versus 0.199). Figure 3 showcases the following:
(A) The prevalence of overall insights, which is defined as the ratio of outputs with at least one insight, across all exams for questions encoded in MC-J format,
(B) The density of insights categorized as accurate or inaccurate, across all exam types for questions encoded in MC-J format.
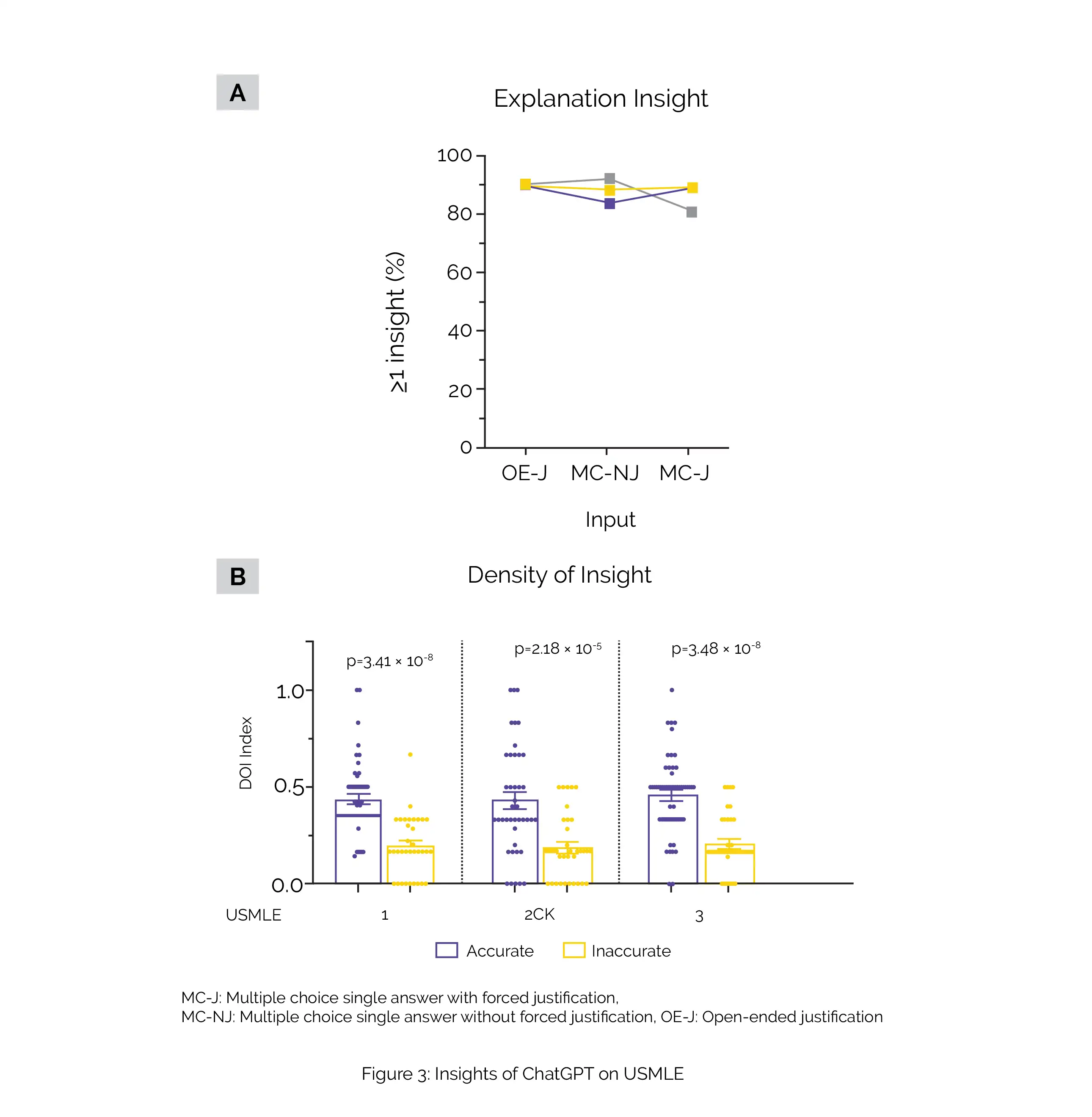
The study findings indicate that large language models like ChatGPT have the potential to assist human learners in medical education, serving as a valuable asset for future integration into clinical decision-making processes. [11]
The creators of ChatGPT acknowledge numerous limitations associated with the model. [3] One of the primary challenges hindering the integration of ChatGPT in healthcare is the requirement for precise and up-to-date data. [15] At times, ChatGPT generates responses that may sound credible but are either inaccurate or nonsensical. Ideally, the model would seek clarification from users when presented with ambiguous queries, but currently, it often relies on guesswork to infer user intent. Despite efforts made to prevent the model from responding to inappropriate requests, there are cases where it may still offer harmful instructions or exhibit biased behavior.
In contrast to search engines like Google, ChatGPT does not actively gather information from the web regarding current events. Its knowledge is constrained to what it learned prior to 2021, resulting in some responses feeling outdated. Chatbots undergo a "training" process using existing text libraries, allowing them to provide responses or output based on specific input from human users. The output is essentially a selection from the training materials, modified by algorithms. Since chatbots lack consciousness, their statements rely solely on rephrasing or rearranging existing content, making their originality unintentional.
Chatbots access the library of texts they were trained on, which poses a risk of verbatim repetition without proper source attribution. In a recent study using ChatGPT, the initial text generated directly from the chatbot had only 6% correct references. Consequently, if chatbot output is to be published in an academic journal, it becomes crucial for the human author and editor to ensure the inclusion of accurate and complete references, akin to the requirements for human authors to evade plagiarism. It is concerning to note that ChatGPT has the potential to deliberately provide false information, as it can fabricate facts despite lacking sentience and knowledge of its own deception due to its programming.
Chatbots lack legal personality and do not possess the status of a legal entity. Consequently, it is not possible to sue, prosecute, or penalize a chatbot in any manner. The terms of use and associated responsibilities for the outcomes resulting from the utilization of the software are defined in the license documentation provided by the software's company. This documentation is akin to the ones produced for other writing tools like Word or PowerPoint. Similar to how Microsoft disclaims responsibility for the content created using Word, the creator of ChatGPT, OpenAI, also disclaims any responsibility for the text generated using their product.
Their terms of use include provisions for indemnity, disclaimers, and limitations of liability. Thus, any errors made by ChatGPT would potentially be the responsibility of its users. Consequently, listing ChatGPT as an author, a practice that is currently being observed and even encouraged, may not be legally justifiable or sound. Although ChatGPT has the potential to be a valuable tool for researchers, it presents a risk to scholarly journals as it can introduce plagiarized or erroneous content into the published literature. Peer review processes may struggle to identify ChatGPT-generated content, as researchers can face challenges distinguishing abstracts produced by ChatGPT from those authored by humans. [3]
It is important to note that ChatGPT may generate inaccurate or biased content. However, users have the opportunity to provide feedback by utilizing the "Thumbs Down" button, allowing ChatGPT to learn from these inputs and enhance its responses accordingly. Furthermore, the responses created by ChatGPT undergo review by AI trainers, who continuously work to ameliorate the performance of the system. The data collected during these interactions is stored securely to protect user privacy and can be deleted upon request. [18]
With ChatGPT, you can create diverse content, from emails to articles and much more. [19] The growing adoption of ChatGPT has triggered a significant upheaval within the scientific community, fueling discussions on the ethical implications of utilizing AI to generate scientific publications capable of impacting the judgments of physicians, researchers, and policymakers. [9] The World Association of Medical Editors (WAME) has issued the following guidelines regarding ChatGPT and chatbots in the context of scholarly publications. [7]
ChatGPT is an evolving technology and OpenAI has already launched multiple iterations of GPT, each exhibiting enhanced speed and features. [15] There is a prompt necessity to establish guidelines governing ChatGPT usage in scientific research, encompassing crucial aspects such as accountability, integrity, transparency, and honesty. Therefore, the ethical and responsible application of ChatGPT in advancing academia and healthcare must be prioritized, considering the associated risks and concerns. Further investigations are required to assess the content of LLMs and their potential influence on advancing academia and science, with a specific focus on healthcare settings.
In the realm of healthcare education, further research is required to assess the potential influence of ChatGPT on the effectiveness and quality of educational content and evaluation tools. Additionally, exploring ChatGPT's utility in enhancing communication skills among healthcare students and utilizing LLMs to better achieve intended learning outcomes through personalized and instant feedback for students are areas that warrant further investigation. [13] With the continuous advancement of AI, the potential applications of ChatGPT in healthcare are poised to expand further.
For instance, by integrating ChatGPT into digital health platforms and robotics, exciting possibilities emerge, such as innovative solutions for RPM, telehealth services, and even robotic-assisted surgeries. Furthermore, ChatGPT can play a valuable role in healthcare-focused podcasts and LinkedIn groups, providing insights, answering inquiries, and fostering collaboration among professionals in the field.
As society looks ahead to the future, it is inevitable that new use cases and developments will arise within healthcare systems. Hence, it is of utmost importance for doctors to remain up-to-date regarding these advancements and delve into the ways AI-powered tools such as ChatGPT can effectively enhance their practices and boost patient care. [4]
ChatGPT is poised to play a crucial role in the future of healthcare development, providing accurate outcomes and precise results. Although the current ChatGPT AI system does not compare its findings with real-world data, the integration of real-world data is anticipated in the future. In various domains, ChatGPT will streamline processes and enhance efficiency. For instance, recruiters can automate hiring steps, saving time and reducing costs. Travelers can conveniently use ChatGPT to book flights, hotels, and other transportation options while obtaining real-time information on weather, local events, and flight statuses. Its unique ability to comprehend and generate human-like text makes it versatile and valuable for various healthcare applications. Whether used for customer support, content creation, or entertainment, ChatGPT is an impressive and beneficial tool.
In the field of healthcare eLearning, ChatGPT holds great potential, from generating informative text to providing personalized learning experiences. To fully harness the capabilities of these technologies, training companies should collaborate with solution providers offering integrated learning platforms driven by generative AI and GPT. As ChatGPT continues to advance, it contributes to the overall progress of AI technologies, pushing the boundaries of deep learning and paving the way for future advancements. [15]
AI has emerged as a dominant force in today's world, steadily gaining traction and becoming a formidable reality. [2] It encompasses the concept of computers learning and taking decisions in a way similar to humans. [3] It includes a broad range of tools, and chatbots are a pivotal part of it. [19] ChatGPT belongs to the category of chatbot applications and serves as a highly capable language model that leverages machine learning algorithms to replicate human-machine interactions. [15] Built upon GPT architecture and extensive language datasets in various languages, this NLP model facilitates real-time conversations with an AI chatbot, enabling it to mimic and generate human-like text responses. [13,15]
The generated responses of ChatGPT are derived from the data it was trained on. Its adaptability spans across various applications, encompassing summarization, translation, and content generation among others. The accessibility of ChatGPT has led to its rapid and widespread adoption due to its remarkable utility. [12] It holds immense potential in revolutionizing the healthcare sector, offering a transformative impact on patient care. [20] In the realm of healthcare, it can generate human-like text to enhance treatment approaches and foster patient understanding of diseases.
This language-based AI model offers a wide range of applications aimed at improving patient experiences and supporting healthcare providers in optimizing medical care practices and accessing valuable information. By facilitating effective communication between medical professionals and patients, it enables better delivery of healthcare solutions that benefit both parties involved. [15] As a valuable tool, it aids clinicians in various aspects and empowers them to boost diagnostic speed and make informed decisions, ultimately leading to advancements in medical practice. [20]
ChatGPT also presents a wide range of possible applications, such as condensing lengthy articles into summaries or assisting in the creation of initial drafts for presentations that can be further refined. It has the potential to aid researchers, students, and educators in generating ideas and even producing reasonably well-written essays on specific topics. OpenAI is currently engaged in the development of an enhanced iteration that surpasses previous versions in generating text, while numerous other companies are also striving to create their own generative AI tools.
As ChatGPT emerges and additional tools are being developed, editors face the need to establish journal policies regarding the utilization of such technology. It is crucial for these policies to mandate the implementation of tools capable of detecting content generated by ChatGPT. [3] It offers a wide range of capabilities, including answering queries, generating both fictional and non-fictional content based on prompts, providing text summaries, and even generating computer code. It has the ability to recall previous parts of a conversation, allowing for follow-up questions, acknowledgement of mistakes, challenging incorrect assumptions, and refusal of inappropriate requests.
The text produced by ChatGPT is generally of high quality, making it an appealing tool for writers seeking instant creation of coherent and logical text. However, it is important to note that there are instances where ChatGPT may generate responses that sound plausible but are incorrect or nonsensical. Additionally, its knowledge is limited to information available prior to 2021, and it lacks awareness of current events. ChatGPT offers the potential for researchers, students, and educators to generate ideas and even produce reasonably well-written essays on specific topics.
While AI can be valuable in various aspects of scientific research, there are significant challenges and limitations when using it for research reports. These include issues of transparency, quality control, ethical considerations, and the potential for amplifying biases present in data and algorithms. It remains crucial to involve human experts in the process to provide context, insights, and result verification. One concerning aspect is the possibility of fraudulent literature being produced by ChatGPT.
The utilization of AI to produce fraudulent scientific research reports has the potential to deceive, fabricate, and serve malicious intents, including distorting scientific discussions and advancing personal motives. This jeopardizes the reliability and trustworthiness of scientific research, potentially resulting in erroneous or detrimental choices influenced by erroneous data. Furthermore, distinguishing ChatGPT-generated abstracts from those written by human authors can be challenging during the peer review process. ChatGPT may be designed to mimic the style and format of genuine reports, making it difficult to identify its contributions.

This highlights the need for caution and thorough evaluation when utilizing AI in scientific research, ensuring that human expertise and critical assessment are integral parts of the process. As an alternative to ChatGPT, Google is developing an upcoming AI chatbot called Bard. [7] Hence, ChatGPT has emerged as a potentially revolutionary breakthrough that could revolutionize human-machine communication. The ramifications of its implementation, however, are yet to be determined, as it can be harnessed for both beneficial and detrimental purposes.
Undoubtedly, it is poised to exert a profound impact on our future. Consequently, it becomes paramount to carefully evaluate the potential benefits and risks associated with this advancing technology and ensure its ethical and responsible use. [15] Further research endeavors can prioritize the development of approaches that effectively address these limitations, all the while capitalizing on the advantages offered by ChatGPT within the healthcare and medical domains. [18]
1. Shahsavar Y, Choudhury A. User Intentions to Use ChatGPT for Self-Diagnosis and Health-Related Purposes: Cross-sectional Survey Study. JMIR Human Factors. 2023 May 17;10:e47564.
2. Khan RA, Jawaid M, Khan AR, Sajjad M. ChatGPT - Reshaping medical education and clinical management. Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences. 2023 Mar-Apr;39(2):605-607.
3. Zielinski C, Winker M, Aggarwal R, Ferris L, Heinemann M, Lapeña JF et al. Chatbots, ChatGPT, and Scholarly Manuscripts-WAME Recommendations on ChatGPT and Chatbots in Relation to Scholarly Publications. Afro-Egyptian Journal of Infectious and Endemic Diseases. 2023 Mar 1;13(1):75-9.
4. What Can ChatGPT Do for Healthcare Practices? Available from: https://www.entrepreneur.com/science-technology/what-can-chatgpt-do-for-healthcare-practices/450626 [Last Accessed On: 9 June 2023]
5. Homolak J. Opportunities and risks of ChatGPT in medicine, science, and academic publishing: a modern Promethean dilemma. Croatian Medical Journal. 2023 Feb 28;64(1):1-3.
6. Haleem A, Javaid M, Singh RP. An era of ChatGPT as a significant futuristic support tool: A study on features, abilities, and challenges. BenchCouncil transactions on benchmarks, standards and evaluations. 2022 Oct 1;2(4):100089.
7. Bhatia P. ChatGPT for academic writing: A game changer or a disruptive tool? Journal of Anaesthesiology Clinical Pharmacology. 2023 Jan-Mar;39(1):1-2.
8. Patel SB, Lam K. ChatGPT: the future of discharge summaries?. The Lancet Digital Health. 2023 Mar 1;5(3):e107-8.
9. Wen J, Wang W. The future of ChatGPT in academic research and publishing: A commentary for clinical and translational medicine. Clinical and Translational Medicine. 2023 Mar;13(3):e1207.
10. Arslan S. Exploring the Potential of Chat GPT in Personalized Obesity Treatment. Annals of Biomedical Engineering. 2023 May 5.
11. Kung TH, Cheatham M, Medenilla A, Sillos C, De Leon L, Elepaño C et al. Performance of ChatGPT on USMLE: Potential for AI-assisted medical education using large language models. PLOS Digit Health. 2023 Feb 9;2(2):e0000198.
12. Parikh PM, Talwar V, Goyal M. ChatGPT: An online cross-sectional descriptive survey comparing perceptions of healthcare workers to those of other professionals. Cancer Research, Statistics, and Treatment. 2023 Jan 1;6(1):32-6.
13. Sallam M. ChatGPT utility in healthcare education, research, and practice: systematic review on the promising perspectives and valid concerns. InHealthcare 2023 Mar 19 (Vol. 11, No. 6, p. 887). MDPI.
14. Implications of ChatGPT for Healthcare. Available from: https://www.abstractivehealth.com/implications-of-chatgpt-for-healthcare
[Last Accessed On: 9 June 2023]
15. Javaid M, Haleem A, Singh RP. ChatGPT for healthcare services: An emerging stage for an innovative perspective. BenchCouncil Transactions on Benchmarks, Standards and Evaluations. 2023 Feb 1;3(1):100105.
16. Revolutionizing Healthcare: The Top 14 Uses Of ChatGPT In Medicine And Wellness. Available from: https://www.forbes.com/sites/bernardmarr/2023/03/02/revolutionizing-healthcare-the-top-14-uses-of-chatgpt-in-medicine-and-wellness/?sh=59efd31d6e54
[Last Accessed On: 8 June 2023]
17. Cheng K, Li Z, He Y, Guo Q, Lu Y, Gu S et al. Potential Use of Artificial Intelligence in Infectious Disease: Take ChatGPT as an Example. Annals of Biomedical Engineering. 2023 Jun;51(6):1130-1135.
18. Dave T, Athaluri SA, Singh S. ChatGPT in medicine: an overview of its applications, advantages, limitations, future prospects, and ethical considerations. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence. 2023;6.
19. How is ChatGPT used in healthcare: benefits and use cases. Available from: https://chatfuel.com/blog/chatgpt-in-healthcare [Last Accessed On: 9 June 2023]
20. The Future of ChatGPT in Healthcare: Potential Applications. Available from: https://www.datasciencecentral.com/the-future-of-chatgpt-in-healthcare-potential-applications/ [Last Accessed On: 8 June 2023]
Comments (0)