Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Using Ibuprofen-containing foam dressing in people having superficial second-degree burns eligible for outpatient follow-up offered effective pain management and boosted patient comfort. It did not show a negative effect on wound healing, as elucidated from a recent study. Investigators aimed to assess the effectiveness of a foam dressing containing Ibuprofen in treating partial-thickness burns.
A total of 50 patients having superficial second-degree burn wounds participated. In this prospective randomized clinical study, 25 patients received an Ibuprofen-containing foam dressing, while 25 patients served as controls and received a paraffin-coated gauze dressing. Thirty minutes after dressing, the visual analogue score (VAS) was assessed. The Vancouver scar scale (VSS) was given to the patients on the 90th day after the wound had healed in order to assess the healing and formation of scar.
Compared to the control group, Ibuprofen-containing foam dressing group exhibited a significantly increased rate of wound healing, decreased frequency of dressing change, and lower oral analgesic needs and VAS scores, as shown in Table 1:
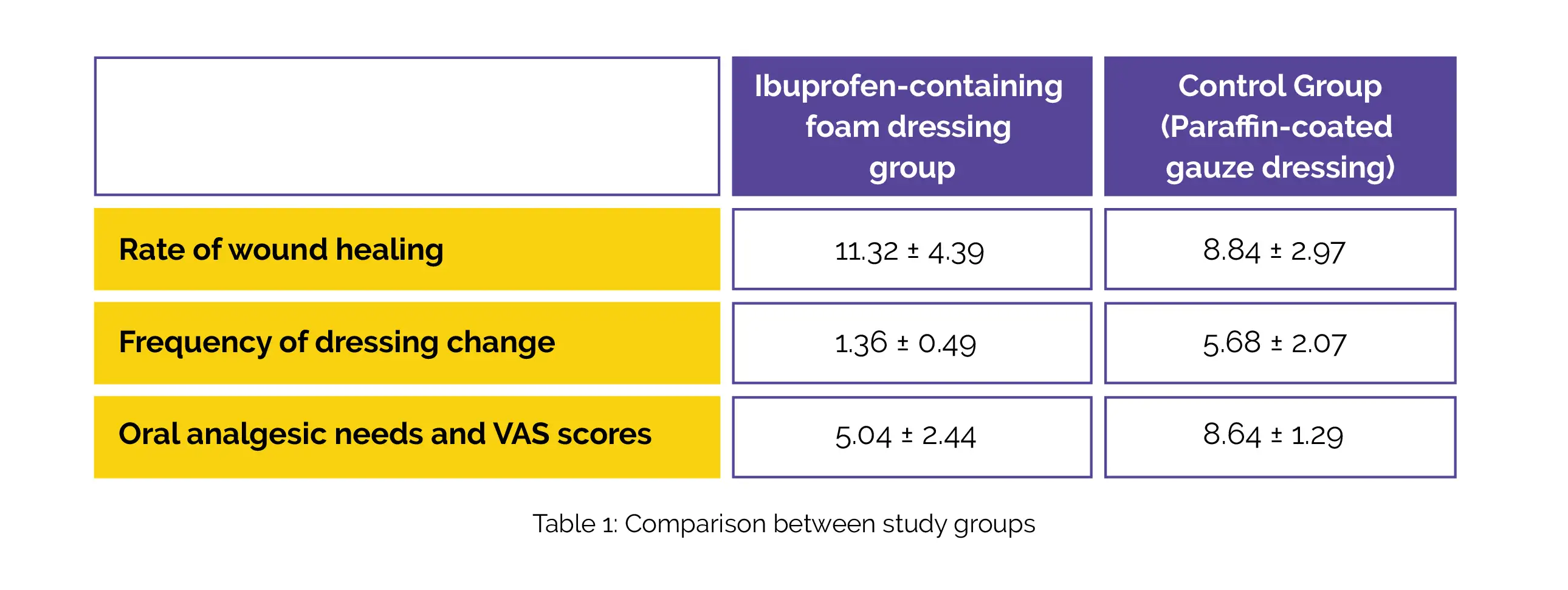
In terms of VSS, the total score was reduced in the study group. However, no noteworthy differences were noted. Therefore, topical application of Ibuprofen is beneficial to relieve partial-thickness burn wounds.
Wound Management & Prevention
Pain Management With Topical Ibuprofen in Partial-Thickness Burn Wounds and Effects on Wound Healing: A Prospective Randomized Clinical Study
Ali Emre Akgun et al.
Comments (0)