Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


This single-center, prospective, randomized clinical trial sought to compare the safety and effectiveness of a new Vonoprazan-based regimen with the Bismuth-based quadruple regimen for H. pylori management.
The Vonoprazan-based regimen exhibited comparable efficacy as the Bismuth-based quadruple regimen in H. pylori-infected people.
This single-center, prospective, randomized clinical trial sought to compare the safety and effectiveness of a new Vonoprazan-based regimen with the Bismuth-based quadruple regimen for H. pylori management.
Patients with H. pylori who were treatment-naive were randomly allocated to either the BASE group (220 mg Bismuth two times a day, 1000 mg Amoxicillin, 500 mg Clarithromycin, and 20 mg Esomeprazole) for fourteen days, or the VAS group (Vonoprazan 20 mg two times a day, Amoxicillin 750 mg thrice a day, and S. boulardii 250 mg two times a day) for ten days. At least 4 weeks following therapy, a 13C-urea breath test was utilized to evaluate the elimination success, and adverse events were noted. Cost-effectiveness evaluations and factors related to eradication success were also carried out.
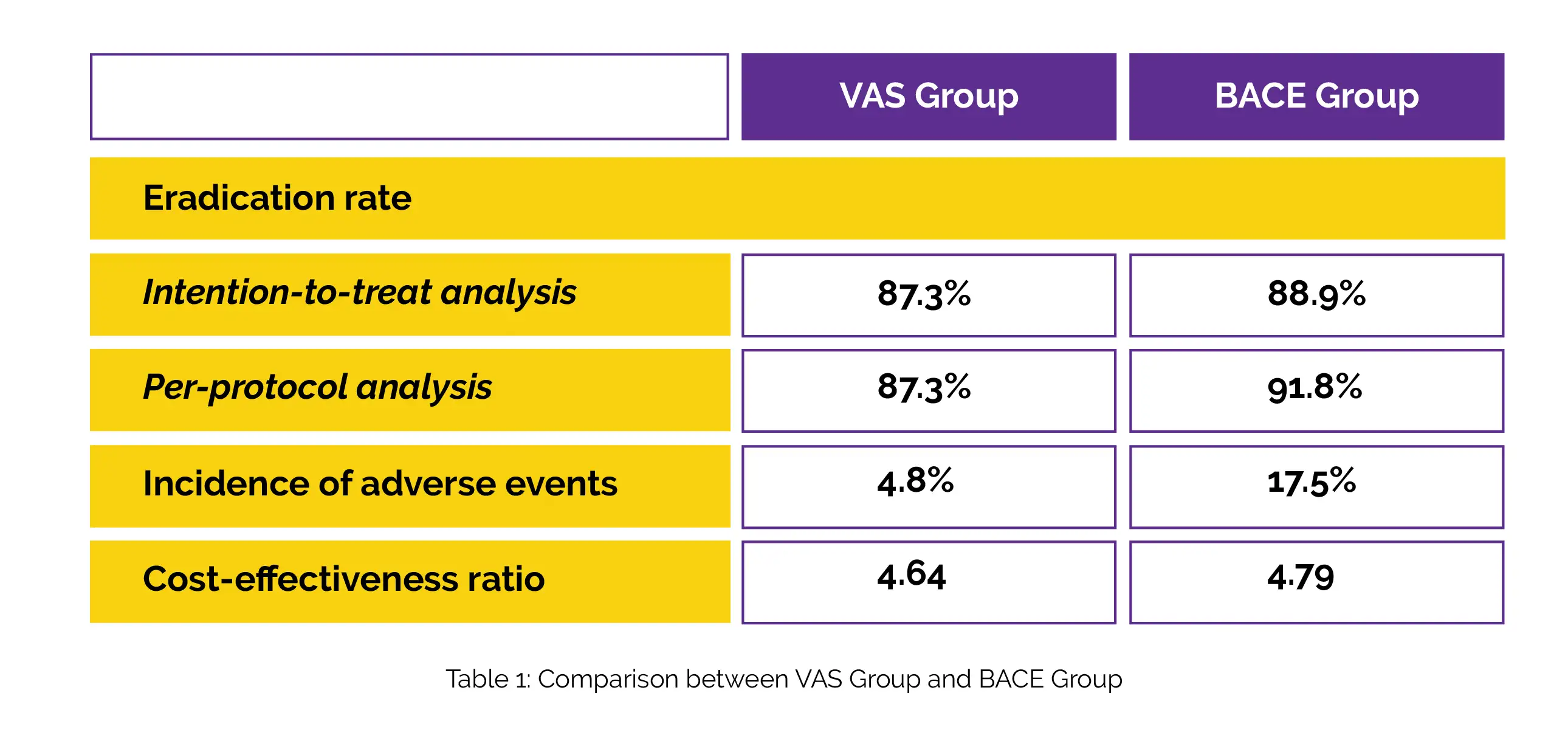
After 135 people were screened, 126 were randomly selected. Table 1 displays the eradication rates for the VAS and BACE groups using both per-protocol analysis and intention-to-treat analysis. In contrast to the VAS group, the BACE group experienced a much greater rate of adverse events. The VAS group's cost-effectiveness ratio was lower than the BACE group's.
In the VAS group, non-smokers (eradication rate: 92.9% in non-smokers vs. 42.9% in smokers) and patients with a small body surface area (BSA) (eradication rate: 92.2% in people with BSA less than 1.831 vs. 66.7% in patients with BSA ≥ 1.831) were more likely to experience successful H. pylori eradication.
For H. pylori management, the Vonoprazan-based regimen is as efficient as the Bismuth-based quadruple regimen. It is more cost-effective, has fewer side effects, and is better suited to people with low BSA and who do not smoke.
Gut
IDDF2022-ABS-0149 Effectiveness and safety of novel Vonoprazan-based regimen for H. pylori eradication in china: a single-centre, prospective, randomized trial
Xiaoyong Wang et al.
Comments (0)